
Catalog # AP2041
Atrogin-1 Antibody
Rabbit Polyclonal
| ELISA | 1:2000 |
| IHC | 1:100 |
| WB | 1:1000 |
Size 100 μl
Species Reactivity Hu, Rt, Ms
MW 41 kDa
Atrogin-1/Muscle Atrophy F-box (MAFbx) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that mediates proteolysis events that occur during muscle atrophy. This ATP-dependent ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis occurs in response to a variety of catabolic states in muscle. Atrogin is expressed in heart and skeletal muscle, and is upregulated during muscle atrophy. In addition, Atrogin expression increases in C2C12 myotubes after stimulation with cytokines. Atrogin is thought to recognize and bind to some phosphorylated proteins and promote their ubiquitination and degradation during skeletal muscle atrophy. Atrogin interacts with MyoD by ubiquitination via a sequence found in transcriptional coactivators and therefore may play an important role in the course of muscle differentiation by determining the abundance of MyoD. Mice deficient in Atrogin are resistant to muscle atrophy.
References
Dai, K.S. & Liews, C.C. (2001) J Biol. Chem. 276(26):23992.
Leger, B. et al. (2006) J Physiol. 576(3):923.
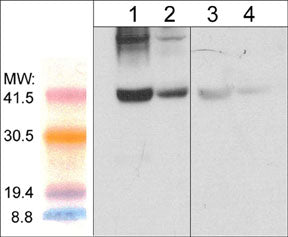
Western blot image of mouse gastrocnemius (lanes 1 & 3) and mouse diagphram tissue lysate (lanes 2 & 4). The blot was probed with anti-Atrogin-1 (AP2041; lanes 1-4) in the presence (lanes 3 & 4) or absence (lanes 1 & 2) of Atrogin-1 peptide (AX2045).

Formalin fixed, citric acid treated parafin sections of E16 mouse skeletal muscle. Sections were probed with anti-Atrogin-1 (AP2041) then anti-Rabbit:HRP before detection using DAB. (Images provided by Carl Hobbs and Dr. Pat Doherty at Wolfson Centre for Age-Related Diseases, King's College London).
*For more information, see UniProt Accession Q9CPU7
The products are are safely shipped at ambient temperature for both domestic and international shipments. Each product is guaranteed to match the specifications as indicated on the corresponding technical data sheet. Please store at -20C upon arrival for long term storage.
*All molecular weights (MW) are confirmed by comparison to Bio-Rad Rainbow Markers and to western blot mobilities of known proteins with similar MW.
Product References:
Yin, J. et al. (2018) Nat Commun. 9:1752. (WB: mouse myotubes)Zhang, Y. et al. (2017) Evid Based Comp Altern Med. 6268378. (IHC: mouse gastrocnemius)
Riaz, M. et al. (2016) PLoS Genet. May; 12(5): e1006031. (WB: mouse myotubes)
Buhler, A. et al. (2016) Int J Mol Sci. 17(2). pii: E187. (IHC: zebrafish skeletal muscle)
Abrigo, J. et al. (2016) Cell Signal. 28(5):366. (WB: mouse C2C12 cells)
Marino, F.E. et al. (2015) JCSM.12031 (WB: mouse gastrocnemius)
Tanaka, M. et al. (2016) Acta Histochem. 118(1):56 (WB: rat soleus muscle)
Nogueira-Ferreira, R. et al. (2016) Int J Cardiol. 203: 858 (WB: rat cardiomyocytes)
Akira, W. et al. (2016) Mol Cell Biochem. 412(1-2):59 (WB: rat gastrocnemius muscle)
Moreira-Gonçalvesa, D et al.(2015) Bioch Bioph 1852(12):2722 (WB: rat blood and gastrocnemius)
Kwon, O.S. et al. (2015) J Appl Physiol 119(10):1033. (ICC: rat diaphram muscle)
Greco, S. H. et al. (2015) PLoS One. 10(7): e0132786. (WB: pancreatic cells)
Son, Y.H. et al, (2015) Journal of Endocrinology 225(1): 27. (WB: C2C12)
Padrao, A. I. et al. (2015) Arch Biochem Biophys. 567:13 (WB: rat cardic muscle)
Toledo, M. et al. (2014) PLoS One. 9(12):e113931. (WB: mouse gastrocnemius)
Mastro, L.M. et al. (2015) Domest Anim Endocrinol. 50:14. (WB: horse gluteus medius muscle)
Joung, H. et al. (2014) Cell Signal. 26(10):2240. (WB: mouse skeletal muscle)
Akkad, H. et al. (2014) PLoS One. 9(4): e92622 (WB: rat masseter muscle)
Smith, IJ et al. (2014) FASEB J. 28(7):2790. (WB: rat diaphragm)
Parreiras-e-Silva, L. et al.(2014) Clin Sci;. 127(3):185. (ICC, WB: C2C12 myotubes)
Ostler, J. et al. (2014) Am J Phys Endo Metab. 306(6): E592. (WB: rat gastrocnemius and skeletal muscle)
Fanin, M. et al. (2014)Muscle Nerve 50(3):340. (WB: human proximal muscle)
van Langenberg, DR et al. (2014) Journal of Crohn's and Colitis 8(7):626. (WB: human muscle)
Wheatley, S. et al. (2014) Am J Phys Endo Metab. 306(1):e91. (WB: pig skeletal muscle)
Puppa, M.J. et al. (2014) FASEB J. 28(2):998 (WB: C2C12 myotubes)
Bobadilla, M. et al. (2014) Stem cells 32(2): 447. (WB: mouse satellite cells)
Tardif, N. et al. (2013) Am J Clin Nutr 98(6): 1485. (WB: human vastus lateralis muscle)
Boutry, C. et al. (2013) Am J Physiol Endo Metab. 305(5):620 (WB: pig skeletal muscle)
Russel, A.P et al. (2013) J Physiol. 591(18):4637. (WB: muscle)
Pond, A.L. et al. (2014) Muscle Nerve. 49(3): 378 (WB: mouse gastrocnemius)
Rovetta, F. et al.(2013)Toxicol Appl Pharmacol;271(2): 196. (WB: C2C12 myotubes)
Banduseela V. et al. (2013) Physiol Genomics 45(12):477. (WB: Porcine skeletal muscle )
Wilkinson, D. et al. (2013) J Physiol. 591(11):2911. (WB: human skeletal)
Dong, Y. et al. (2013) PLoS One 8(3): e58554 (WB: mouse satellite cells)
Kirk-Ballard, H. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8(2):e57112. (WB: C2C12 myotubes and mouse skeletal muscle)
Aare, S. et al. (2013) Physiol Genom. 45(8): 312. (WB: pig biceps femoris muscle)
Fanin, M. et al. (2013) Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol ?? (WB: human skeletal muscle )
Penna, F. et al. (2013) Am J Pathol 182(4):1367. (WB: mouse skeletal muscle)
Dumont, N. & Frennete, J. (2013) Am J Pathol 182(2):505. (WB: mouse C2C12, soleus )
Zhang, G. & Li, Y. (2012) Skeletal Muscle 2:20. (WB: C2C12 myoblasts, mouse skeletal muscle)
Mukai. R. et al. (2012) PLoS One 7(9):e45048. (WB: mouse muscle denervation induced )
This kit contains:








































